Topological Deep Learning
A new way to work with higher-order, complex data in the context of deep learning.
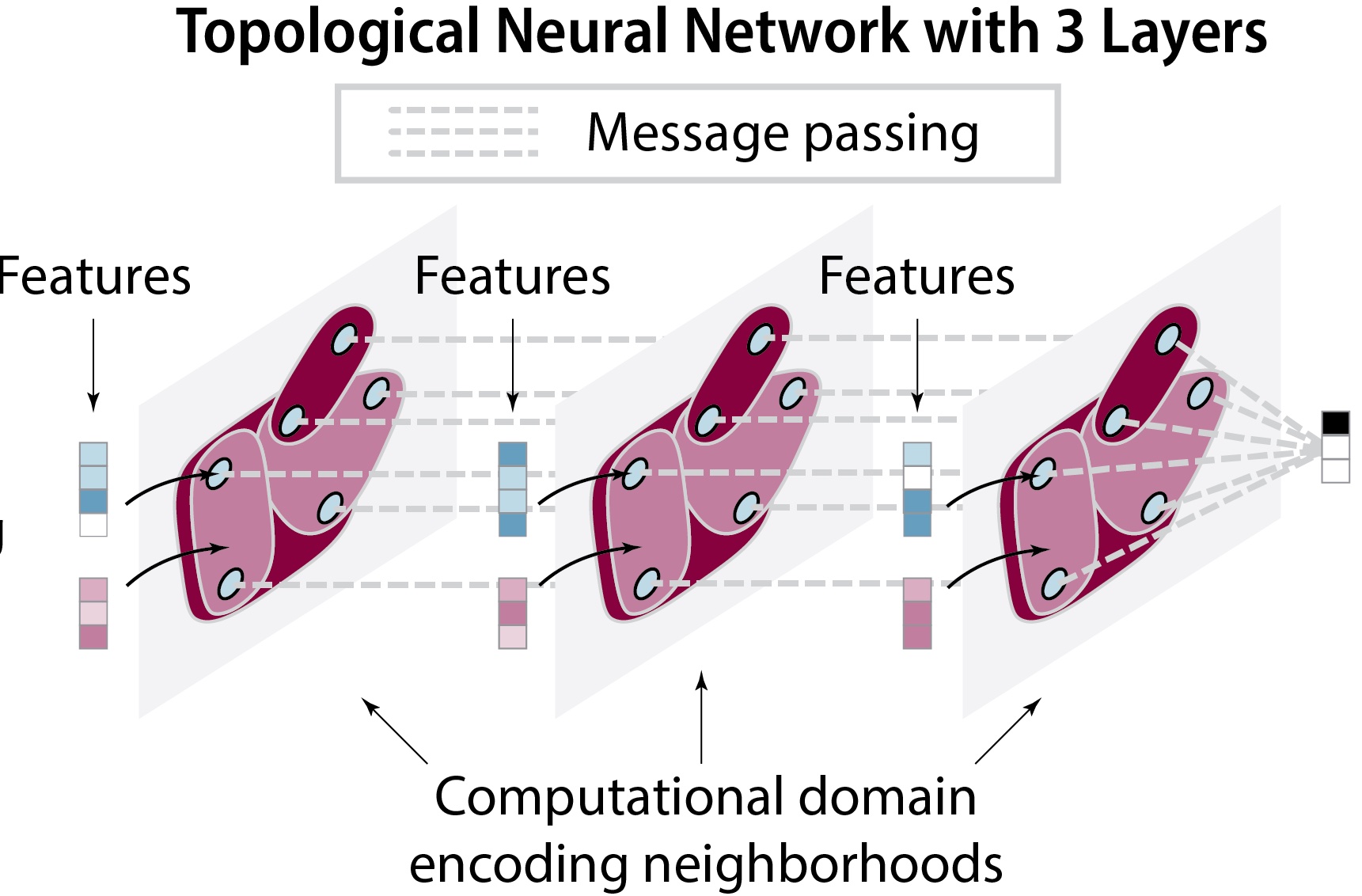
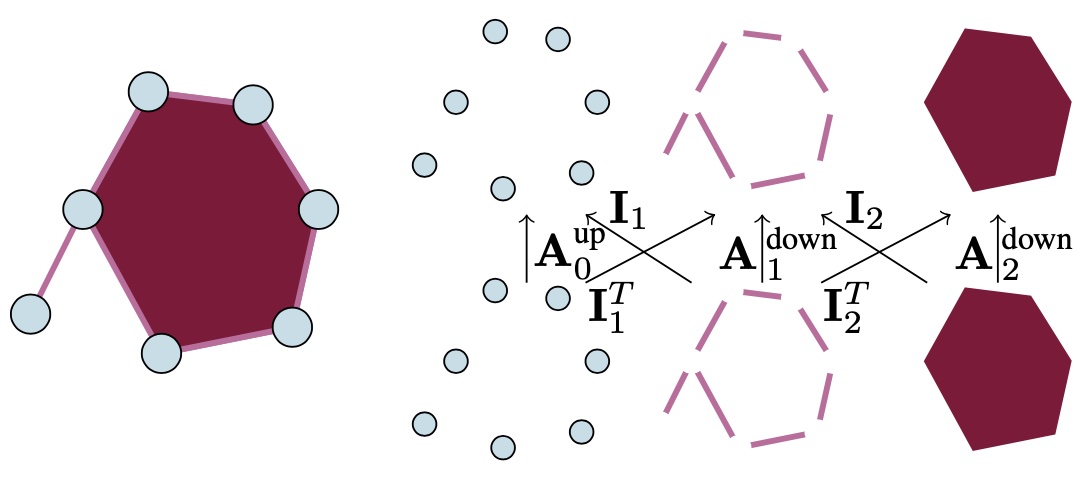
Topological deep learning is a rapidly growing field that pertains to the development of deep learning models for data supported on topological domains such as simplicial complexes, cell complexes, and hypergraphs, which generalize many domains encountered in scientific computations.
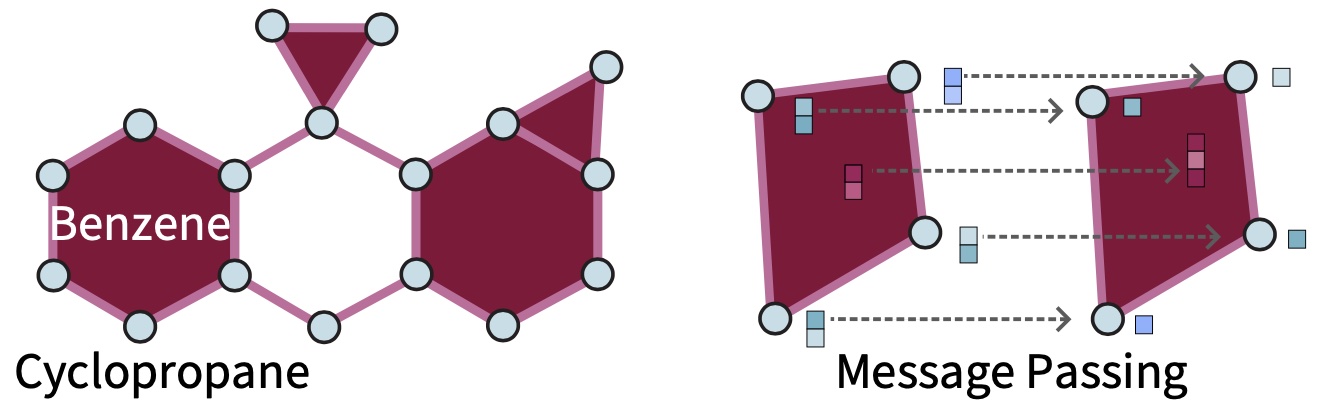
Traditional machine learning often assumes that the observed data of interest are supported on a linear vector space and can be described by a set of feature vectors. However, there is growing awareness that, in many cases, this view- point is insufficient to describe several data within the real world. For example, molecules may be described more appropriately by graphs than feature vectors. Other examples include three-dimensional objects represented by meshes, as encountered in computer graphics and geometry processing, or data supported on top of a complex social network of interrelated actors. Hence, there has been an increased interest in importing concepts from geometry and topology into the usual machine learning pipelines to gain further insights into such types of data in a systematic way.
TDL is concerned with algebraic-topology integrated into deep learning frameworks. Topology is concerned with the study of properties that remain invariant under continuous deformations, and affords a powerful lens through which the global structure of data can be discerned. By characterizing topological features (including connected components, loops, and voids across multiple scales), topological tools such as persistent homology (Carlsson, 2009; Edelsbrunner & Harer, 2010) have become powerful methods to capture essential structures and patterns that elude conventional methods.
Going beyond the existing paradigm of persistent-homology, four practical advantages of TDL are as follows. First, the topology of the underlying data space determines the choice of possible neural network architectures. Second, topological domains enable the modeling of data containing multi-way interactions (also known as higher-order relations). Third, TDL captures regularities inherent to manifolds, such as ‘remeshing symmetry’. Fourth, TDL captures topological equivariances in the data. In summary, TDL takes into ac- count topological characteristics that appear in relational data, and therefore is a natural choice for various machine learning problems.
Related Publications
2023
2023
-
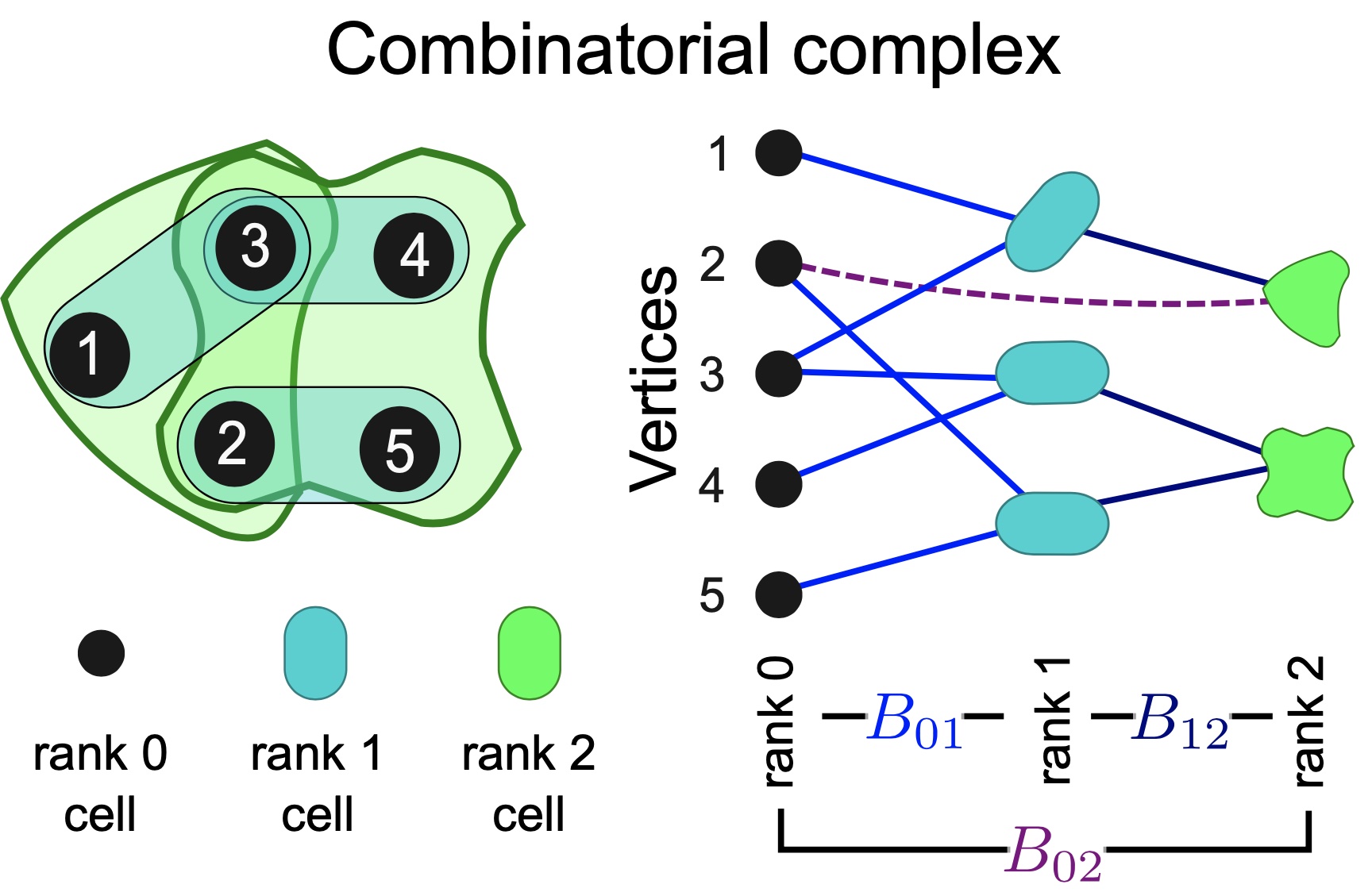 Combinatorial complexes: bridging the gap between cell complexes and hypergraphsIn Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, 2023
Combinatorial complexes: bridging the gap between cell complexes and hypergraphsIn Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, 2023
2024
-
 Attending to Topological Spaces: The Cellular TransformerarXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14094, 2024
Attending to Topological Spaces: The Cellular TransformerarXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14094, 2024
2024
-
 Position: Topological Deep Learning is the New Frontier for Relational LearningIn Int. Conf. Machine Learning (ICML), 2024
Position: Topological Deep Learning is the New Frontier for Relational LearningIn Int. Conf. Machine Learning (ICML), 2024